MQTT
Collecting data through MQTT to supOS is supported. During the process, supOS is acting as the MQTT broker and a client.
Adding Collector
- Log in to supOS, and then click
 at the upper-right corner to go to the design center.
at the upper-right corner to go to the design center. - Select Collection Node Management > Authentication.
- Click
 , and then enter the corresponding information to add a collector.
, and then enter the corresponding information to add a collector. - Set the Style to IOT gateway, and select the Timestamp to be recorded in the data.
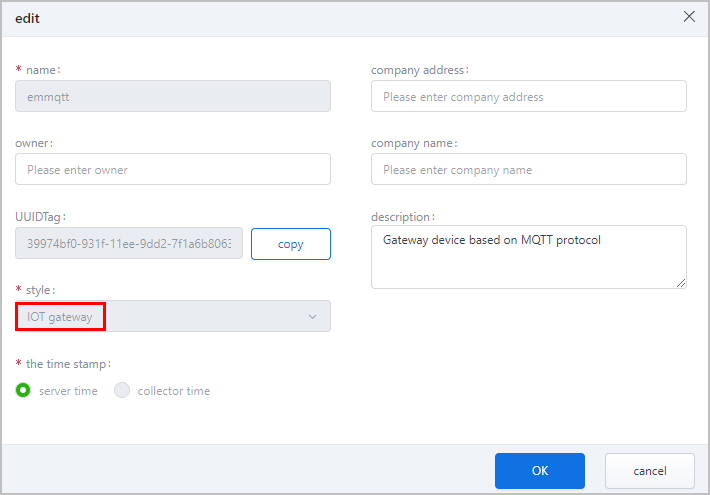
- Click OK.
Configuring MQTT Connection
Connecting MQTT Client
- On the MQTT client, connect to the supOS.
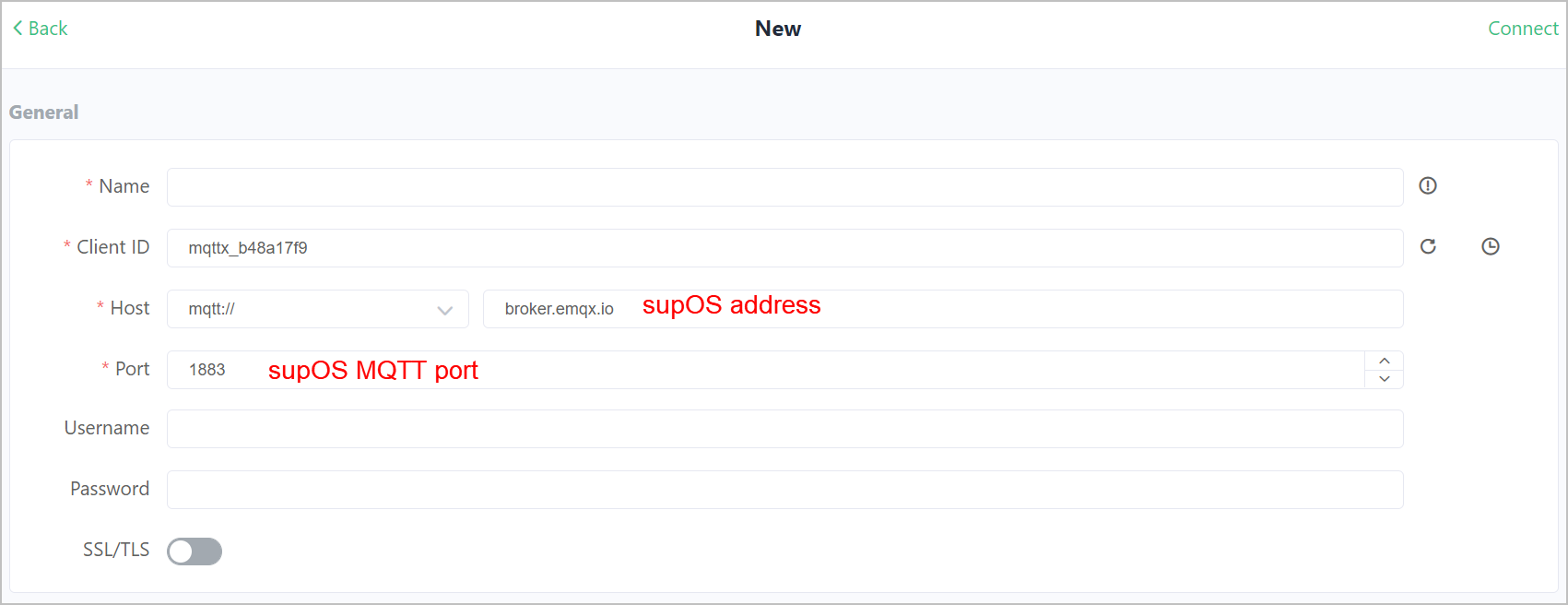
info
The port set for supOS MQTT broker is 32566.
- Set the topic
/{auth token}/{endpoint id}/{endpoint name}/{method name}/{direction}to send tag data to supOS according to MQTT Integration.infoDifferent topics for different requests have been defined.
Encoding MQTT Message
info
- Data encoding protocol is using
ProtoBuf. Only encoded data can be received and parsed by supOS. - Encoding program can be diversified. In this section, Python is used as an example.
- Copy the data protocol you need from MQTT Data Protocol and paste to a XXX.proto file in PyCharm.
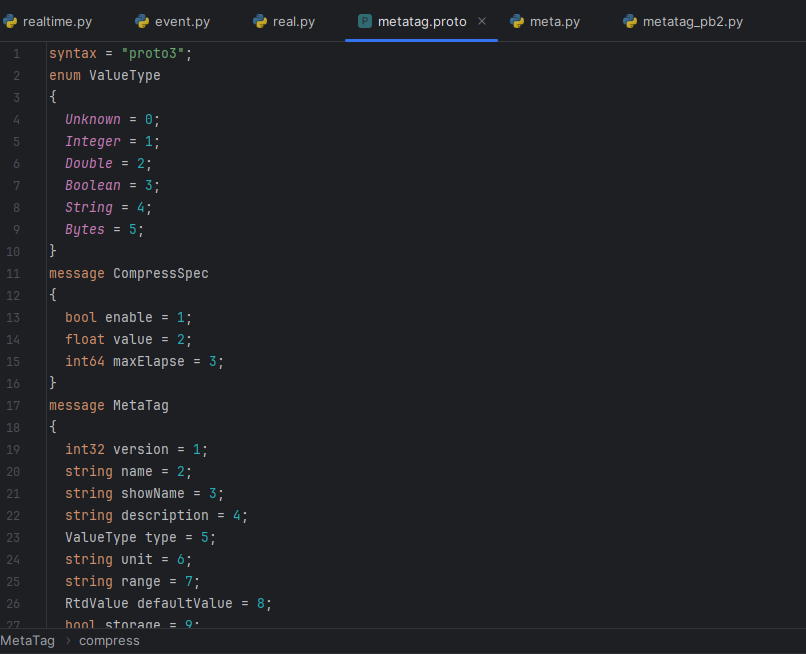
- Download protoc-25.1-win64.zip file from Github.
- Decompress the package and add the .bin path to system environment variables through This PC > Properties > Advanced system settings.tip
You can use
protoc --versionin CMD to check whether it is successfully downloaded. - Use protoc to compile the data protocol defined by supOS.
protoc -I=$SRC_DIR --python_out=$DST_DIR $SRC_DIR/XXX.proto
info
For details, see Python Tutorial.
- Use the generated XXX_pb2.py file to write a script to encode the tag data.
import binascii
import metatag_pb2
# Create a MetaTagSequence
metatag = metatag_pb2.MetaTagSequence()
# Create and add the first MetaTag
metatag1 = metatag.tags.add()
metatag1.version = 1
metatag1.name = "exampleTag1"
metatag1.showName = "exampleTag1"
metatag1.description = "new"
metatag1.type = metatag_pb2.ValueType.Integer
# Create and add the second MetaTag
metatag2 = metatag.tags.add()
metatag2.version = 1
metatag2.name = "exampleTag2"
metatag2.showName = "exampleTag2"
metatag2.description = "new"
metatag2.type = metatag_pb2.ValueType.Integer
# Serialize the MetaTagSequence
serialized_data = metatag.SerializeToString()
# Print the entire MetaTagSequence and the serialized data in hexadecimal format
print(metatag)
print(binascii.hexlify(serialized_data))
- Copy the serialized code.
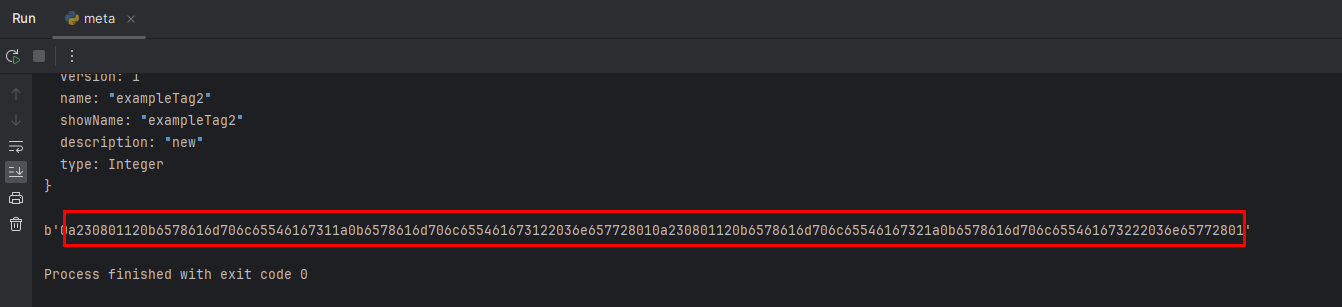
Authenticating Collector
- Paste the encoded code to MQTT client and send it to supOS broker.
- Under Collection Node Management > Status, find the collector node, and click Agree under operation.
- Go to Object Model Management > Object Instance, select Collector Template and find the instance with the name as the collector node you authenticated.
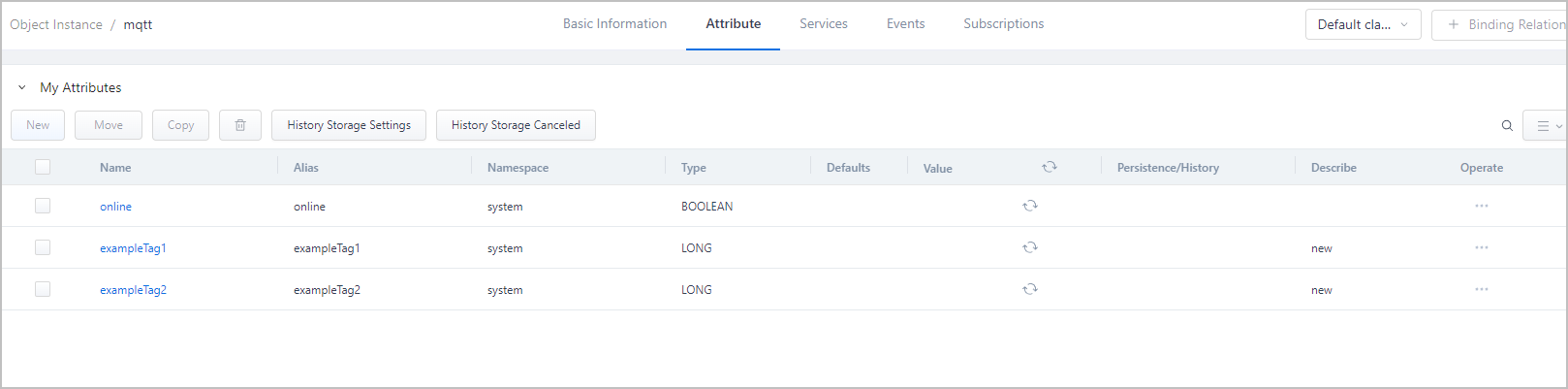
Sending Real-time Data
Encoding Real-time Data
- Encode real-time tag data in Python.
import binascii
import metatag_pb2
# Create a MetaTagSequence
namedvalue = metatag_pb2.ValueSequence()
# Create and add the first MetaTag
rtdvalue1 = namedvalue.values.add()
rtdvalue1.name = "exampleTag1"
rtdvalue1.value.dblVal = 89
rtdvalue1.value.quality = 2
rtdvalue2 = namedvalue.values.add()
rtdvalue2.name = "exampleTag2"
rtdvalue2.value.dblVal = 32.59
rtdvalue1.value.quality = 8
# Serialize the MetaTagSequence
serialized_data = namedvalue.SerializeToString()
# Print the entire MetaTagSequence and the serialized data in hexadecimal format
print(namedvalue)
print(binascii.hexlify(serialized_data))
- Copy the code and paste it to MQTT client as message.
- Set the topic
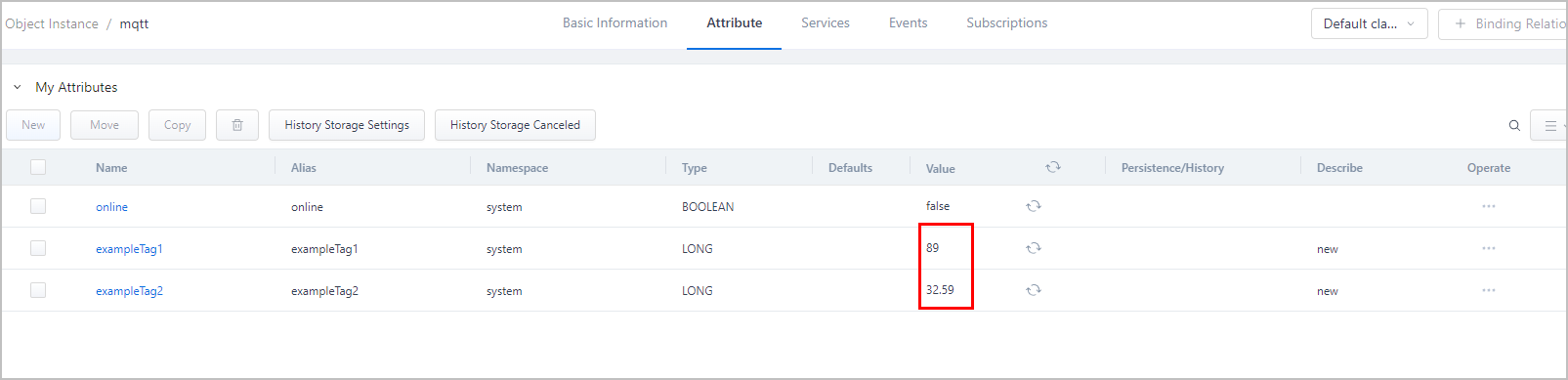
/{auth token}/{endpoint id}/{endpoint name}/rtdvalue/report, and send the message to supOS. - Check the instance attribute values to see if they match.tip
Hover over the attribute value to check the quality code (Status Code).